Gum Grafting
Gum grafting is a surgical procedure that can regenerate, rejuvenate, and restore gum tissue that has been lost due to gum recession, and prevent further damage.
Table of Contents
Gum Grafting and Gum Recession
Gum grafting (or soft tissue grafting/augmentation) is a surgical procedure to treat, reverse, and prevent gum recession (gingival recession). In order to understand gum grafting, you need to understand the condition it treats – gum recession.
Gum recession (gingival recession) is a condition when the gum tissue pulls away from the tooth, exposing the tooth root. Preventing and treating recession is important for many reasons. When gums recede, not only is soft tissue being lost, but the bone that should be covering and supporting the root is lost as well. When too much bone and tissue has receded, the teeth lose its support and can become loose. Teeth roots are not designed to be exposed to the oral cavity, and thus are less resistant to tooth decay and from normal wear and tear of daily function. Because of this, meticulous oral hygiene is necessary to prevent root decay, and fillings may be necessary to cover exposed roots. Root caries (decay of the tooth roots) is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in the elderly population, with over 30% of people over the age of 60 having at least one tooth with root decay.
Gingival recession can be caused by many factors. Some of these are inherited/genetic, such as being born with thin gum tissue, thin underlying bone, high/aberrant frenum attachments, or malpositioned teeth. Some factors are environmental, such as tooth movement/orthodontics, bacteria/periodontal disease, improper dental work/restorations, improper habits/oral hygiene techniques, etc. In most cases, it is a combination of factors that contribute to gum recession. For example, teeth that are malpositioned or crowded will often have thin underlying bone/tissue. Because of the crowding and the thin tissue, it is difficult to keep the area clean, which causes more plaque or bacteria in the area which causes more inflammation. All of these factors contribute to gingival recession.
The most important thing to treat gingival recession is to identify the factors predisposing or causing the recession and modifying them to prevent further recession in the future. Quite often, thin gum tissue in the area of the recession is a presdisposing factor for future recession. This is because thin gum tissue is delicate, friable, and prone to damage from everyday wear and tear. Thick gum tissue is strong and resistant to future recession. Because of this, gum grafting, or soft tissue augmentation is the treatment of choice.
When this is the case, soft tissue augmentation is the treatment of choice. In a gum grafting procedure, tissue, usually from the roof of the mouth, is placed under the existing gums to thicken them, and then pulled over to cover the exposed roots. The goal of the procedure would be to create thick gum tissue that is strong enough to withstand wear and tear and prevent further recession in the future.
In some cases, recession can cause an esthetic problem with because of exposed tooth roots and an uneven gum line. Treating the factors predisposing to gingival recession is still the primary goal of any soft tissue augmentation procedure. As a secondary goal, we can usually cover part or all of the exposed root during the procedure to create a beautiful smile.
What you should know before your Gum Graft in Orange County
Before having a gum graft, you will first need to have a consultation appointment. At this appointment, a comprehensive evaluation will be performed on your gums to evaluate the health, any gum recession, and what factors may be causing gum recession. The purpose of this appointment is also to determine whether gum grafting is the best treatment for you and how we can prevent your gum recession from getting worse. We are always honest and upfront with you. Unfortunately, gum recession is often an over-treated condition. Not all gingival recession needs to be treated with gum grafting – quite often, close monitoring and instruction and feedback on oral hygiene techniques are more than enough to prevent future recession. If we do not believe you are in need of gum grafting, we will discuss other options to treat your gum recession. If you are a good candidate for gum grafting, we will discuss the goals and expected results of the treatment.
What happens during your Gum Graft procedure?
What kind of anesthesia is used?
Most of the time, we do gum grafts under local anesthesia. The area is numbed just like any other dental procedure. We also offer two additional sedative options. An oral sedative or anxiolytic can be prescribed for you to take an hour before the procedure, which will help calm you down and make you drowsy during the procedure. You may or may not remember the procedure afterward. Another sedation option we offer is “twilight” anesthesia. A board-certified dental anesthesiologist will administer medication through an IV line to make sure you are safely sedated and asleep during the entire procedure.
The surgical procedure
Gum grafting is a delicate and precise surgery. We use 5.5x magnification and microsurgical blades to make the smallest incisions and use microsurgical sutures in order to create the most esthetic outcomes with minimal discomfort. We utilize minimally invasive techniques such as VISTA or holes to tunnel underneath the existing gum tissue in the area to be treated for gum rejuvenation (not to be confused with the Pinhole Gum Rejuvination, which is registered trademark). Sometimes a small strip of tissue is carefully removed from the palate and carefully tucked under the gum tissue. Fine microsurgical sutures are used to pull the tissue to cover over and against the root.
How long is the Gum Graft procedure appointment?
Depending on how many teeth are being treated, the gum graft appointment is usually around 1.5 hours to 3 hours long, but the actual procedure time is shorter.
Gum Graft recovery and results: what to expect
After the anesthesia wears off, you may feel slight tendernessor soreness in the site, but there should be very little pain. Any discomfort can be controlled with over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol). You may experience some swelling or bruising in the area for up to 72 hours, which will slowly improve over time. By one week, most of the swelling will have subsided. Most patients can go back to work the next day. The only restriction is heavy lifting or exercise for the first few days.
It is imperative that the surgical area remain as still as possible – that means no chewing or biting foods in the area and no brushing, as it may alter the outcomes of the procedure.
The stitches we use are dissolvable and some may get loose and fall off around 1 week. If tissue is taken from the palate, a liquid bandage will be placed in the area to protect the site as it heals. It will typically fall off after a week. We usually see you for a post-operative check around 2-3 weeks after the procedure and remove any stitches that are still there. We will usually give you a special post-operation toothbrush to start brushing with and see you for another check after 1 month.
Most of the initial healing occurs in the first two weeks, which is when the graft is most fragile and the most care is needed. The next four weeks afterwards is when the inflammation subsided and the soft tissue matures and blends in. Because of the delicate microsurgical techniques and materials we use, not only is there minimal discomfort afterward, but superior healing. Our soft tissue grafts are like fine wine – they get better over time. As the tissue matures, it will continue to blend in and appear more esthetic. The gums will thicken and stay protective of future recession, and in many cases continue to “creep” upwards to cover the root even after many years, a phenomenon called creeping attachment.
Before and After Photos
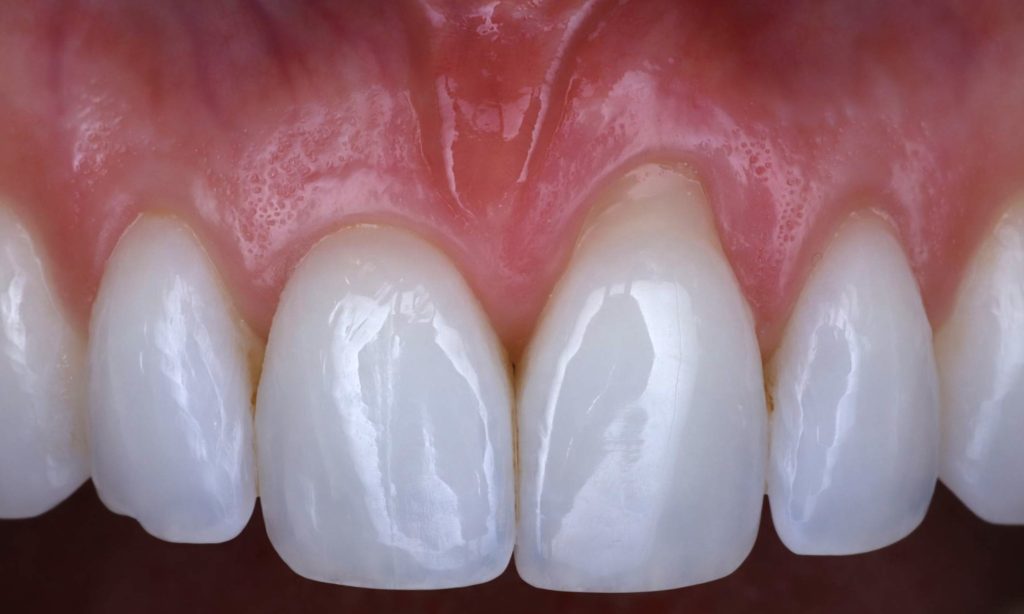
Before: Recession on a front tooth, making the gums uneven and an esthetic nightmare.
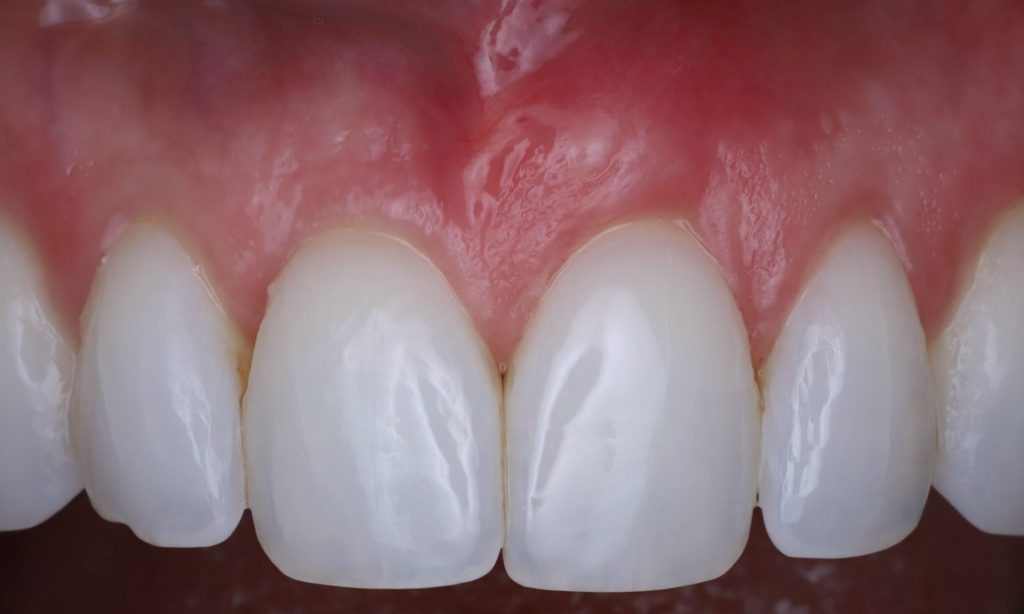
After: Soft tissue grafting covering up the exposed root and creating an esthetic outcome. Tissue blending will improve as it continues to heal.
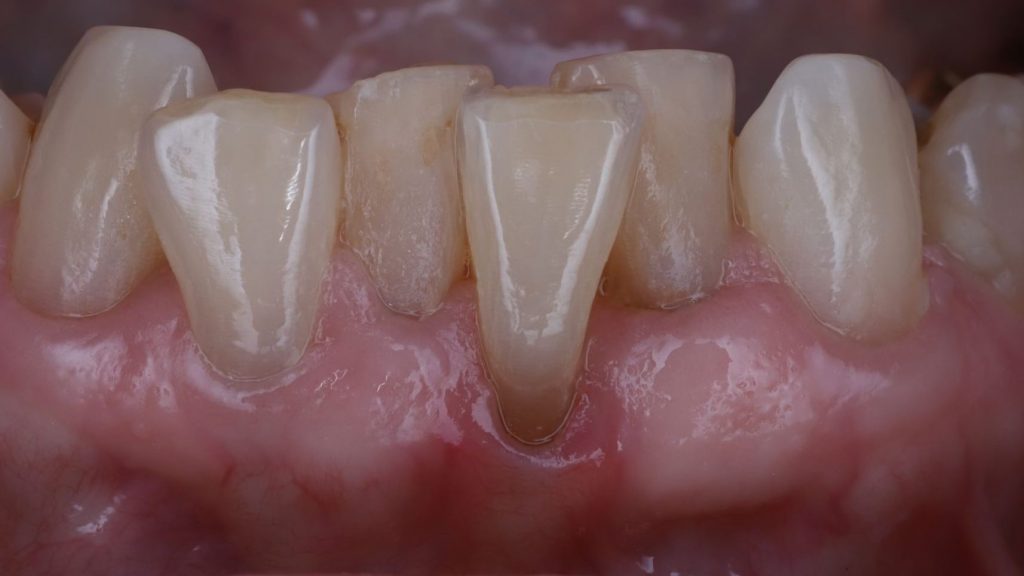
Before: Thin tissue with gum recession, dark root, and tooth malposition.
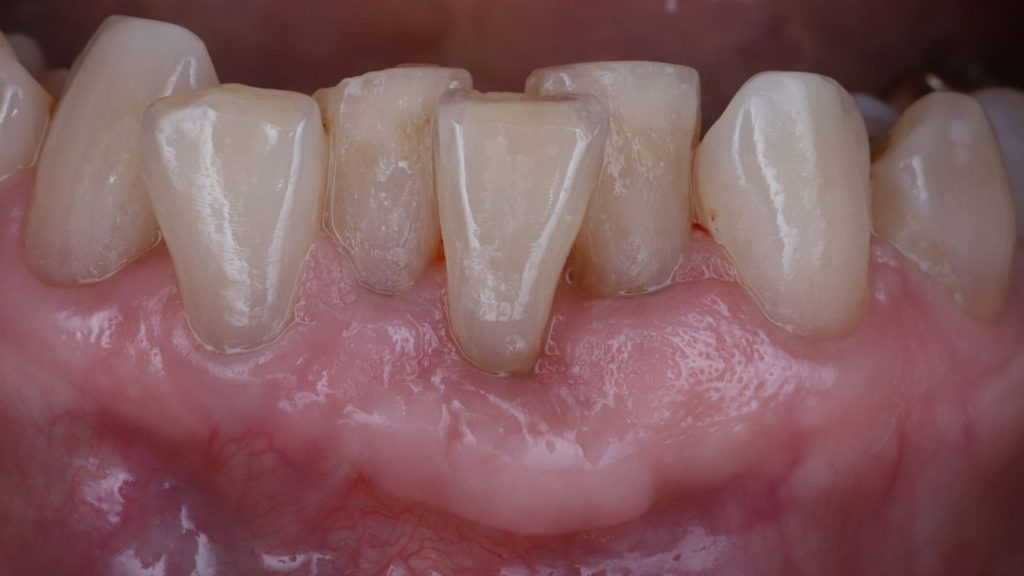
After: Gum tissue covering the entire root, that is thick and protective but also well blended in.
Our team of periodontists specialize in soft tissue and gum grafts, and serve the communities of Orange County, including Orange, Anaheim, Fullerton, Anaheim Hills, Tustin, Placentia, Yorba Linda, Santa Ana, Villa Park and Garden Grove. Book your consultation today!
